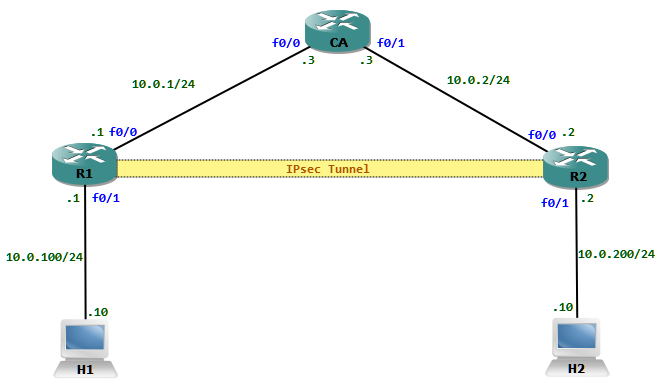
All communication between H1 and H2 must be protected with IPsec.
Tasks to do
- Synchronize the time
- Configure IOS CA Server
- Enroll routers to attain certificates
- Classify interesting traffic
- Configure ISAKMP Phase 1 policy and IPsec Phase 2 Transform set
- Create a crypto map and apply crypto map to interface
Step 1: Time must be synchronized for certificates to work properly. The CA router could be configured as a NTP master which then will provides time to other routers. Continue reading »